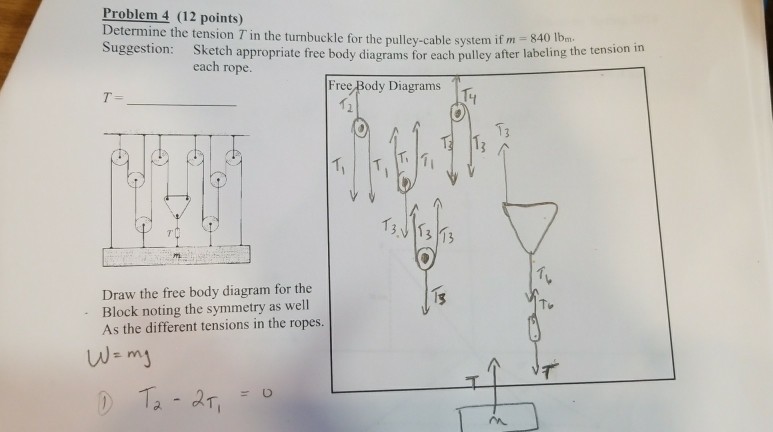
Free Body Diagram Tension Pulley
When discussing ropes strings etc. Free body diagram of a pulley.
Solved Problem 4 12 Points Determine The Tension T In T Chegg Com
First we will draw the free body diagram for the block.
Free body diagram tension pulley. Free body diagram of a pulley. A 50kg block is placed on top of a 10kg block. A free-body diagram and determine the vector sum of all forces acting on an object.
In this course it will generally be assumed that they have zero mass and do not stretch. Free body diagram for pulley the only two forces acting on the pulley are the two tensions. T1 and t2 represent the tension.
1 Free body diagram of m 1 W 1 the weight of m 1 T 1 the tension of the string at m 1 force exerted by string on m 1 a 1 vector acceleration of m 1 W 1 T 1 m 1 a 1 Newtons second law vector equation W 1 0 -W 1 T 1 0 T 1 a 1 0 a acceleration assuming. We know that this pulley system will accelerate when released so we shouldnt expect the net forces acting on the bodies in the system to be zero. A Draw a free body diagram for each pulley b Find tension in each section of rope T1T2T3T4 c Find the magnitude of T1.
The pulleys are massless and frictionless. You can assume that the rope is massless and inextensible and that the pulley is frictionless. Theory When two masses are suspended by a string over a pulley Figure 1 each feels a downward force due to its weight Wmg and an upward force due to the tension T in the string Figure 2.
Find the upward acceleration of the smaller mass and the tension in the rope. A The free-body diagram of the red box. Free body diagram for up.
Draw a simple picture called a Free Body Diagram and label your axes. Your free body diagram should end up looking something like the figure below. Draw a fbd of the 1000 lb weight.
A mass M is held in place by an applied force F and a pulley system as shown in figure. The torque from is the cross product of the radius vector with. Live tv from 60 channels.
á l û f ú l ù û e ú l ü l û l ú. Find the tension on each string. Free-body diagrams if there is no friction.
A free body diagram is a picture showing the forces that act on a. û ù ú h ù. Force mg will act in the downward direction due to gravitational pull and tension will act in the opposite direction ie.
Free body diagram of a pulley. In an ideal system the massless and frictionless pulleys do not dissipate energy and allow for a change of direction of a rope that does not stretch or wear. Correctly include tension forces arising from massless ropes in free body diagrams.
A 0 T W mg 5 kg98 ms 49 N y -y Weight W Tension. Making accurate free body diagrams for a system of blocks connected by string and pulleys is an important step towards writing the correct equations of motion. The pulleys are massless and frictionless.
The free body diagram helps you understand and solve static and dynamic problem involving forces. Describe the tension in a rope that passes over a massless pulley. If these two forces are equal then the net.
Department of Mechanical Engineering Force equilibrium mechanical eql Mechanical equilibrium requires that the concurrent forces that act on the body satisfy The particle in a equilibrium system must satisfy Since both must be satisfied the material point then must have zero acceleration a. Draw a fbd of the hook assembly c. Use your drawing to write down Newtons 2nd law F Net ma T - W 2 0 In equilibrium everything is balanced.
The torque from is the cross product of the radius vector with. D and e a. Making accurate free body diagrams for a system of blocks connected by string and pulleys is an important step towards writing the correct equations of motio.
Start with a good free-body diagram. Assume the pulley is frictionless and massless which means the tension is the same everywhere in the string. Two masses of 80 kg and 140 kg hang from a rope that runs over a pulley.
Free body diagrams The mechanical advantage of a pulley system can be analysed using free body diagrams which balance the tension force in the rope with the force of gravity on the load. Identify and draw all force vectors Step 3. Two masses on a pulley.
A mass M is held in place b. Whats the net torque. The tension forces are resolved in the horizontal and vertical directions.
C The free-body diagram of the red box with force components aligned with the coordinate system. If the pulleys and strings are ideal then the tension in the string on either side of a pulley is the same unless the term fixed pulley means that the wheel does not rotate and friction is present. Two in fact one for each mass.
In this case their behavior is fairly simple. You need to first understand all the forces acting on the object and then represent these force by arrows in the direction of the force to be drawn. Draw a free body diagram of bar ac below.
B An appropriate coordinate system for the red box. Well learn how to account for the pulley later in the course. The organic chemistry tutor 29819 views.
Find the tension on each string. T1 and t2 represent the tension of the string and their magnitudes are equal. T1 sina T2 sinb mg -1 T1cosa T2cosb2.
It is a diagram including all forces acting on a given object without the other object in the system. Pulley free body diagram and rope tension. A diagram for the system of two objects and a pulley.