Free Radicals Oxygen
The key difference between free radicals and reactive oxygen species is that free radicals may or may not contain oxygen atoms whereas reactive oxygen species essentially contain oxygen atoms. We usually use the terms free radicals and reactive oxygen species interchangeably because reactive oxygen species are always free radical compounds.

What Is A Free Radical Primonutra
The two most important oxygen-centered free radicals are superoxide and hydroxyl radical.

Free radicals oxygen. This radical is partly stable in anoxic environment but under normoxic condition its unpaired electron is given to oxygen and superoxide radicals are formed. Reduction of an electron from ring C in ANT causes to formation of free radical semiquinone. During the first two-three decades after ROS discovery in biological systems 1950-1970 years.
Effect of Free Radicals on the Body. The phrases free radicals and reactive oxygen species ROS are frequently used interchangeably although this is not always correct. Once free radicals are generated whether through exposure to a carcinogen or doing the normal processes of body metabolism they are free to do damage.
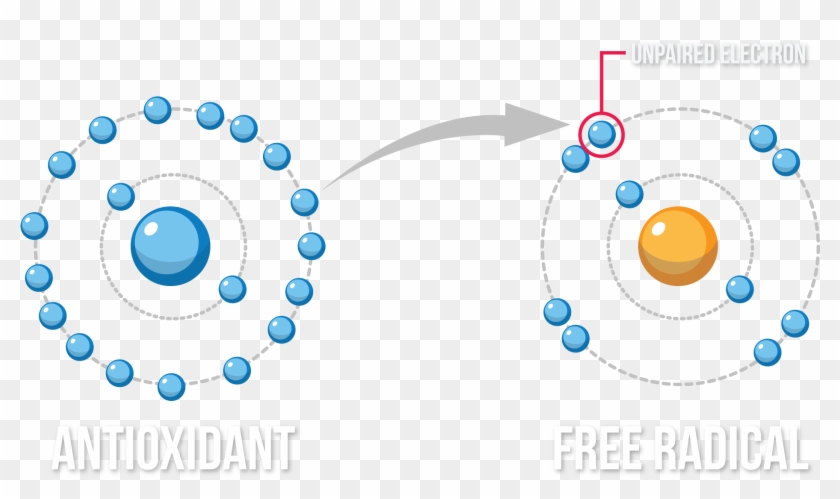
Atoms with a full outer shell are stable but free radicals are unstable and in an effort to make up the number of electrons in their outer shell they react quickly with other substances. The availability of free radicals creates what is known as oxidative stress in the body. The reason it is named oxidative stress is that the reactions that occur which result in free radicals obtain an electron are done in the presence of oxygen.
Oxygen metabolism in living cells and many factors such as environmental pollutants radiation and pesticides inevitably lead to the formation of oxygen free radicals. Oxygen free radicals are known to depress Ca binding and uptake of sarcoplasmic reticulum which would lead to a decrease in the myocardial contractility. They cause direct cell damage increase vascular permeability through damage to the capillary endothelium and promote chemotaxis.
Free Radicals and Reactive Oxygen. Its true that the increased amount of oxygen brought into the body with oxygen therapy causes a small amount of oxidation and the production of free radicals especially in our lungs. Oxygen free radicals eg nitric oxide superoxide and hydroxyl radical are implicated in the tissue damage observed in RA.
This article gives a brief description of two mentioned oxygen forms. A radical often but unnecessarily called a free radical is an atom or group of atoms that have one or more unpaired electrons. Oxygen free radicals are released during the respiratory burst phase of phagocytosis by neutrophils and macrophages during inflammation.
63 Antioxidants including vitamin E α-tocopherol vitamin C ascorbic acid β-carotene and selenium may have a protective role against tissue. The main ones of these radicals are. The major OFRs include the superoxide radical hydroxyl and hydrogen peroxide.
They derive from molecular oxygen under reducing conditions. Oxygen free radicals OFRs are probably one of the earliest and most important components of tissue injury after reperfusion of ischemic organs. We have shown that oxygen free radicals depress cardiac function and cardiac contractility.
Semiquinone Radicals 285 Words 2 Pages. However because of their reactivity these same free radicals can participate in unwanted side reactions resulting in cell damage.
Free Radicals Theory Of Aging
The free radical theory of aging postulates that aging changes are caused by free radical reactions. The free radical theory of aging asserts that many of the changes that occur as our bodies age are caused by free radicals.
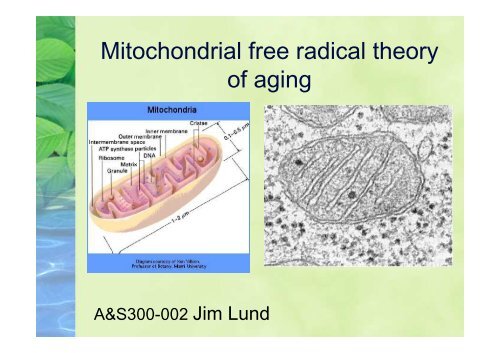
Mitochondrial Free Radical Theory Of Aging
Aging is a complex set of processes that involve a diverse set of conditions and reactions.
Free radicals theory of aging. The free radical theory of aging conceived in 1956 has turned 40 and is rapidly attracting the interest of the mainstream of biological research. Damage to DNA protein cross-linking and other changes have been attributed to free radicals. The free radical theory of the aging process is based on the hypothesis that with increasing age mutations of the mitochondrial DNA will accumulate and will at least lead to a loss of function with subsequent acceleration of cell death.
Aging and the degenerative diseases associ-ated with it are attributed basically to the dele-terious side attacks of free radicals on cell con-stituents and on the connective tissues. It is also why there are multiple theories on the process of aging. The mitochondrial theory of aging C.
The extensive studies based on this possibility hold promise that the ALE-B can be extended to 85 years and the maximum life span increased. The cross-link theory of aging. Over time this damage accumulates and causes us to experience aging.
From its origins in radiation biology through. The data supporting this theory indicate that average life expectancy at birth may be increased by 5 or more years by nutritious low caloric diets supplemented with one or more free radical reaction inhibitors. Growing evidence indicates that random free radical reactions are a major factor in the breakdown of such systems suggesting that the aging process may be simply the sum of these everpresent deleterious reactions throughout the cells and tissues and that longevity is a reflection of the ability to cope with such reactions.
According to the free radical theory of aging first outlined in 1956 free radicals break cells down over time. Aging changes may be caused by free radical reactions. The Free Radical Theory This now very famous theory of aging was developed by Denham Harman MD at the University of Nebraska in 1956.
Aging is the apparently unavoidable decrease in physiologic function that happens after some time. The amassing of various degrees of damage to the cells and the genetically programmed process of. As the body ages it loses its ability to fight the effects of free radicals.
Redundancy is a key for understanding aging and the systemic nature. The Mitochondrial Free Radical Theory of Aging MFRTA proposes that mitochondrial free radicals produced as by-products during normal metabolism cause oxidative damage. Even if this theory is widely accepted the reactive-oxygen-species-induced mutations of mitochondrial DNA the accumulation of mitochondrial DNA and the role of.
The free radical theory of aging FRTA B. This is why the aging process has been very difficult to define. There is some evidence to support this claim.
Reliability theory allows researchers to predict the age-related failure kinetics for a system of given architecture reliability structure and given reliability of its componentsApplications of reliability-theory approach to the problem of biological aging and species longevity lead to the following conclusions. At least four main theories of aging have been discussed that imply to clarify much or majority of the reason of biological aging. Match the theory of aging to the corresponding method to help slow down the aging process according to that theory.
The free radicals probably arise largely through reactions involving molecular oxygen catalyzed in the cell by the oxidative enzymes and in the connective. Group of answer choices. It posits that aging results from free radical damage to mitochondrial DNA that is caused by reactive oxygen species ROS generated within the mitochondria during complex I electron transport.
Hormonal stress theory Choose exercise meditation increase consumption of fruits and vegetables Free radical theory. According to MFRTA the accumulation of this oxidative damage is the main driving force in the aging process. The mitochondrial free radical theory of aging is currently one of the more widely accepted theories to explain the aging process.
Definition The free-radical theory of aging was formally proposed by Denham Harman in 1956 and postulates that the inborn process of aging is caused by cumulative oxidative damage to cells by free radicals produced during aerobic respiration. The processes of aging can be divided into two groups. The term free radical describes any molecule that has a free electron and this property makes it react with healthy molecules in a destructive way.
Oxygen Derived Free Radicals
Gastric damage was assessed by blood-to-lumen leakage of 51Cr-EDTA as well as by measuring the extent of macroscopically visible hemorrhagic lesions. Oxygen-derived free radicals.

Biochemistry Of Reactive Oxygen And Nitrogen Species Intechopen
The role of oxygen-derived free radicals in the pathogenesis of acute gastric ulceration induced by indomethacin Indo was investigated in rats.

Oxygen derived free radicals. Department of Surgery Creighton University Omaha Neb. We have expanded the study of these substances to include measurements of. It is now clear that oxygen-derived free radicals play an important part in several models of experimentally induced reperfusion injury.
Thus the endothelial balance tips towards vasoconstrictor responses over the course of diabetes. Oxygen-derived free radicals have been implicated as possible mediators in the development of tissue injury induced by ischemia and reperfusion. Elevated levels of endotoxin oxygen-derived free radicals and cytokines during extracorporeal membrane oxygenation.
Recent evidence suggests that oxygen-derived free radicals may be abundantly produced in ischemic tissues accounting for at least part of the damage that resultsWhat exactly. These experiments demonstrate that oxygen-derived free radicals generated by activated xanthine oxidase appear to play a central role in the pathogenesis of acute pancreatitis in these models. Oxygen-derived free radicals not only reduce nitric oxide bioavailability but also facilitate the production andor action of EDCFs.
Following curative surgery for carcinoma of the sigmoid colon at Dukes stage C 198 patients making an uneventful recovery from surgery were randomized to the control group or to receive allopurinol 50 mg. Oxygen-derived free radicals formed during metabolic activities may readily initiate chain reactions that can damage cellular membranes and release intracellular components eg. Elevated levels of oxygen-derived free radicals are the initial source of endothelial dysfunction in diabetes.
Oxygen-derived free radicals in postischaemic tissue injury N Engl J Med 1985. The influence of scavengers of oxygen-derived free radicals on survival in colonic cancer was studied. In all experimental models the increase in the gastric erosions and in TBA reactants in the gastric mucosa.
Lysosomal enzymes leading to further tissue injury in addition to degradation of hyaluronic acid the principal component of the epithelial basement membrane and cross-linking proteins lipids and nucleic acidsH. Oxygen-derived free radicals an atom or atom group having an unpaired electron on an oxygen atom typically derived from molecular oxygen. Oxygen-derived free radicals may be generated when prostaglandin G 2 is converted to prostaglandin H 2 or when 15-hydroperoxy prostaglandin E 2 is converted to prostaglandin E 2.
Oxygen-derived free radicals are very important mediators of cell injury and death. Hinder RA 1 Stein HJ. Trace element status Se Zn Cu in heart failureKalp yetersizliginde eser elementlerin statusu Se Zn Cu.
Clamping of the celiac artery in rats reduced the gastric mucosal blood flow to 10 of that measured before the clamping. Although there are certainly multiple components to clinical ischemic and reperfusion injury it appears likely that free-radical production may make a major contribution at certain stages in the progression of the injury. Oxygen-derived free radicals and postischemic myocardial dysfunction stunned myocardium.
However under certain circumstances univalent reduction can occur with transfer of only one electron e resulting in the release of highly reactive free radical. Boni L Benevento A Shimi SM. Free radical production in the esophago-gastro-duodenal mucosa in response to acid and bile.
These findings shed light on the fundamental pathophysiology of this disease and may provide the basis for more effective therapy in the future. Gastric damage was assessed by blood-to-lumen leakage of 51Cr-EDTA as well as by measuring the extent of macroscopically visible hemorrhagic lesions. I n the mammalian cell molecular oxygen is essential for energy production through oxidative phosphorylation.
Under normal circumstances most of the molecular oxygen undergoes tetravalent reduction to water by the following intracellular cytochrome oxidase system. The viability of soft tissues in elderly subjects undergoing hip surgery In our last issue we referred to so-called oxygen free-radicals actually known as oxygen-derived free radicals or oxygenated free radicals or just plain free radicals and their possible toxic effects on certain tissues. Cell death will rapidly ensue in the absence of oxygen.
Not only are these highly reactive chemical species important in the aging process but they are either directly or indirectly involved in a wide variety of clinical disorders such as atherosclerosis reperfusion injury pulmonary toxicity macular degeneration cataractogenesis and cancer. The role of oxygen-derived free radicals in the pathogenesis of acute gastric ulceration induced by indomethacin Indo was investigated in rats. It has been demonstrated that the initiation of extracorporeal membrane oxygenation ECMO is associated with an increase in the circulating plasma levels of inflammatory mediators.
The present study was undertaken to test the hypothesis that oxygen-derived. The role of oxygen-derived free radicals and lipid peroxidation in the pathogenesis of acute gastric mucosal erosion was investigated in rat models produced by burn shock stress by treatment with regional hyperthermia platelet activating factor and compound 4880 and by ischemia-reperfusion. For example 1-electron reduction of O 2 produces the superoxide radical Ō 2.
A recent study reported that oxygen-derived free radicals are involved in sevoflurane-induced impairment of endothelium-dependent relaxation. Other examples include the hydroperoxyl radical HOO the hydroxyl radical HO and nitric oxide NO.
